Prefabrication has had a tremendous impact on how the worldwide construction industry has grown over the past few decades. It is preferable over onsite construction because it guarantees the stability, affordability, and environmental performance of the buildings. Everywhere in the world, precast modular buildings are constructed using a variety of techniques. The article thoroughly explores the fundamentals of prefabrication technology, its types, applications, and scope. So keep reading to expand your knowledge of this emerging technology.
What is Prefabrication?
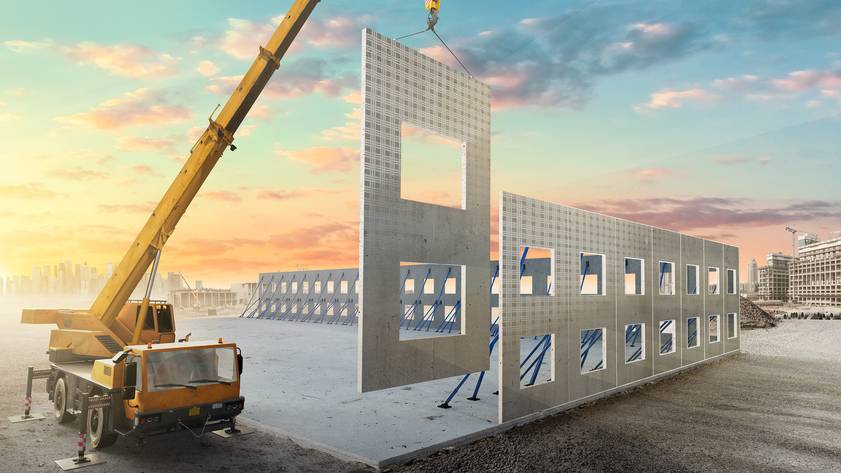
Prefabrication is a technique that can be used to construct buildings or build parts off-site. Using this technology, construction companies can move the finished building to the chosen location, complete the setup, and hand over the establishment to the owners. This off-site construction causes less waste than the traditional acquisition of building materials. Besides, prefabrication lowers labor and material expenses because the components are constructed off-site and are transported completing it partially.
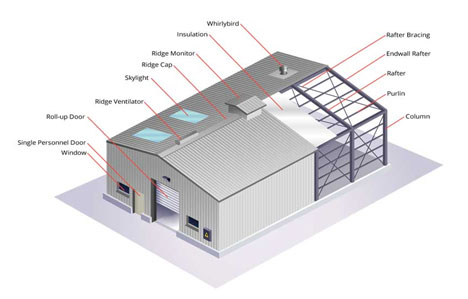
Prefabricated items may include anything from doors to wall panels to floor panels to staircases to windows to walls to roof trusses to room-sized parts and occasionally even whole buildings. Builders all over the world are employing this style of construction to construct high-quality buildings with efficiency and accuracy.
Types of Prefabrication
The common prefabrications techniques employed by industries include:
1. Panelized Wood Framing
These are lengthy frameworks made of laminated wood that is commonly used for roofing which is either covered with plywood or a board roof deck. Roof construction can be done more quickly and safely with the use of panelized frameworks, which can be up to 72 feet long.
2. Sandwich Panels
It is built from two thin facings of a substance like concrete, plywood, or stainless steel. The facings are then joined to an insulating core, which is frequently constructed of foam, paper, fabric, or rubber.
3. Steel Framing
Steel has always been a favorable and reliable building material for both commercial and residential construction. This robust and long-lasting material is utilized in steel frames to produce prefab panels that can be used to build houses.
4. Timber Framing
Timber frame panels, though not particularly widespread in India, but are quite popular in other nations where timber production is more. These framings are constructed in factories and are used to build timber dwellings.
5. Modular Systems
This technology provides a complete building structure that is often comprised of units that are manufactured in a factory using prefabrication only. After being delivered to the construction site, the buildings are simply joined to a prepared foundation.
Applications of Prefabrications
Listed below are some of the common applications of prefabrication technology:
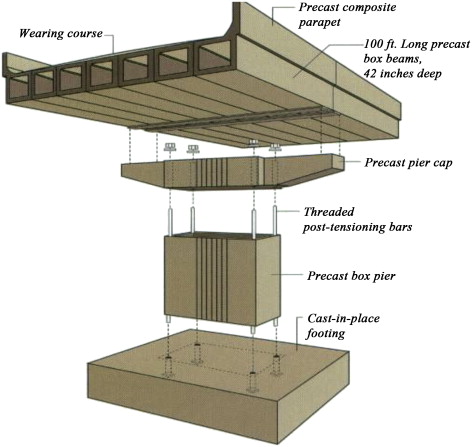
- Prefabricated steel and concrete sections are commonly used forms of prefabrication in buildings and civil engineering when a certain element of a form is duplicated numerous times.
- Apartment buildings and housing projects with several units are built utilizing prefabrication technology.
- Large structures frequently have prefabricated steel and glass components on their exterior.
- After being built and shipped in other nations or states to the final assembly location, prefabricated parts like wings and fuselage sections are now being frequently employed in the building of aircraft and spacecraft.
Scope of Prefabrication Technology
Prefabrication is becoming more and more popular in the Indian construction industry. Prefabricated homes in India have led the way for cutting-edge and inventive construction and designing techniques for all types of buildings including high rises, low rises, villas, and large townships. Due to the government’s accelerated infrastructure construction, there is now a significant and relatively huge demand for building supplies like concrete. Precast concrete now holds the largest market share due to the rise in off-site construction operations. It is expected to rise along with growing non-residential and residential construction due to increased urbanization. Given the expanding scope of prefabrication, there are many potential career options in this field in the near future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of prefabrication technology is revolutionizing the construction industry, offering numerous benefits such as enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved sustainability. As urbanization continues to drive the demand for innovative building solutions, mastering prefabrication techniques is essential for aspiring professionals. By enrolling in CADD Centre courses, you can gain invaluable skills and knowledge in prefabrication, preparing you for exciting career opportunities in this rapidly evolving field. Embrace the future of construction and unlock your potential with CADD Centre’s expert training programs!
FAQs
What are the benefits of using prefabricated components?
The benefits of using prefabricated components include reduced construction time, lower labor costs, improved quality control, and decreased environmental impact due to minimized waste and efficient resource usage.
What materials are commonly used in prefabricated construction?
Common materials used in prefabricated construction include concrete, steel, wood, and composite materials. Each material offers distinct advantages, depending on the project’s requirements and design specifications.
What career opportunities are available in prefabrication?
Career opportunities in prefabrication include roles such as prefabrication design engineer, project manager, construction supervisor, and quality control specialist. The growing demand for prefabricated construction techniques opens various career paths.
How do CADD Centre courses prepare students for careers in prefabrication?
CADD Centre courses provide practical training in prefabrication techniques, covering topics such as design software, construction processes, and project management. This training equips students with the skills needed for a successful career in the construction industry.
Are there any challenges associated with prefabrication?
While prefabrication offers many advantages, challenges include transportation logistics, the need for precise engineering and design, and potential difficulties in integrating prefabricated components with traditional construction methods.
What is the future of prefabrication in the construction industry?
The future of prefabrication in the construction industry looks promising, with increasing adoption due to urbanization, sustainability goals, and the need for efficient building methods. As technology continues to advance, prefabrication is expected to play a pivotal role in shaping modern construction practices.