Wireless Power Transfer (WPT), is a highly commercialized domain and is currently one of the most sought fields of study. Devices including mobile phone chargers, stationary EV chargers, and dynamic EV chargers (also known as road-powered EV chargers, or RPEVs) have all been developed using WPT with notable breakthroughs. The WPT business is expected to expand over the next few decades based on the current rate of technological advancement.
According to projected development trends, it would be advantageous to be familiar with this technology to get a competitive edge in the business sector. Hence, to familiarize you with this burgeoning technology, the article addresses the foundational elements of WPT technology. Keep reading to explore more about WPT.
What is Wireless Power Transfer?
Wireless power transfer is the movement of electrical energy without the use of cables as a physical link. This technology uses induction coils to transport electrical energy wirelessly (or WPT) over an air gap from a power source to an electrical load. These coils create an electromagnetic field that transmits energy with complete galvanic isolation from a charging base station (the transmitter) to a coil on a portable device (the receiver). The receiver coil then transforms the electromagnetic field’s energy into electrical energy.
Wireless power transfer is useful for powering electrical devices in circumstances where connecting wires would be uncomfortable, risky, or impossible. By eliminating the need for wires and batteries, WPT technology can increase the mobility, comfort, and security of an electronic gadget.
Applications of Wireless Power Transfer
The WPT technology finds application in various domains, some of which are illustrated below.
Electronic Portable Devices
Smartphones, laptops, tablets, and even wearable technology are owned and used by billions of people worldwide. What binds all these devices together and enables mobile use, is the necessity to recharge the internal battery. With WPT, the conventional portable gadget can be disrupted and reimagined without the need for a physical power source. Additionally, it will reduce the cost of using mobile devices, make them more comfortable for consumers, and make them safer (power cords can cause fires and electric shocks). Studies have even been done on the possibility of establishing a network of WPT employing multi-hop WPT systems, in which a generator distributes power wirelessly to targets that can then serve as a source for other targets and transmit power wirelessly to those targets.
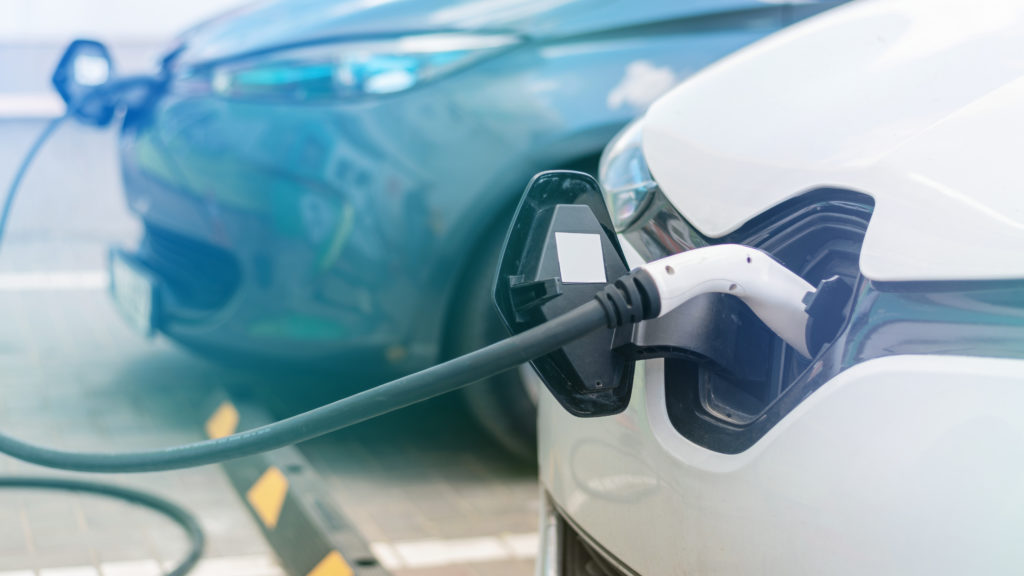
Electric Vehicles
As public awareness of global warming and greenhouse gas emissions grows, electric vehicle use increases. However, the application of electric vehicles is limited by their battery capabilities. Electric vehicles currently require a plug-in connection to replenish their internal batteries, which takes several hours. However, experts predict that in the not-too-distant future, a driver will simply need to leave their vehicles in a certain position in their driveway for the vehicle to charge wirelessly and automatically. These projections are based on several WPT studies, notably those that focus on the MPT process and how it might be used to charge electric vehicles.
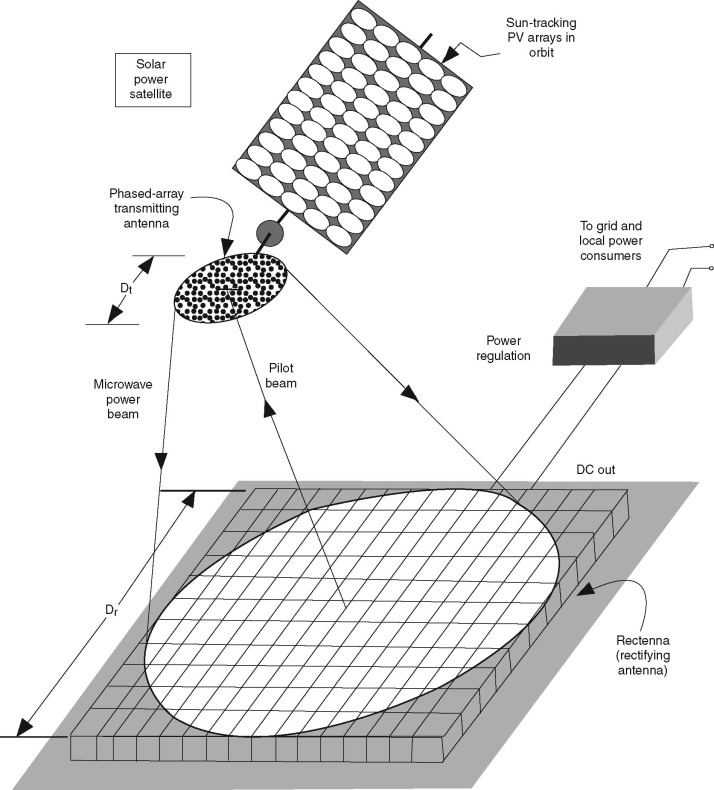
Solar Power Satellites
Solar Power Satellites (SPS), the WPT’s most significant use, produce power by putting satellites with enormous solar arrays in geosynchronous Earth orbit and sending the generated energy back to Earth as microwaves.
Scope of Wireless Power Transfer
Wireless charging is now supported by many devices than simply smartphones and smartwatches. Its scope increases continuously. The focus is on its use in micro and small-scale industries and other fields. The market’s size is increasing significantly on a global scale as a result.
According to Allied Market Research, this industry’s growth rate from 2020 to 2027 would be roughly 23.4%. A $49,304 million market will exist globally by 2027. In India, its market is prominently growing by 14.5 percent. Further, the scope of this technology is growing outside of the electronics sector, in the automotive, industrial, healthcare, aerospace, and defense industries.
Conclusion
In this technological era, we witness innovations and technological upheavals almost every day. This digital economy is propelled by these discoveries. Wireless power transfer is one such revolutionary development in this area that has the potential to change the course of the electric sector. Therefore, to gain a competitive edge in the labor market, it is wise to arm oneself with the knowledge and skills to use emerging technology. So, acquire knowledge in top electrical design programs and grow your opportunities in this fast-growing industry.
FAQs
What is Wireless Power Transfer (WPT)?
Wireless Power Transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without the need for physical wires. It uses electromagnetic fields to transfer power from a transmitter to a receiver, enabling devices to charge or operate wirelessly.
What are the key applications of Wireless Power Transfer?
WPT is used in a variety of applications, including charging smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and even solar power satellites. It enhances convenience and safety by eliminating the need for physical cables.
What industries are most impacted by WPT?
WPT is revolutionizing multiple industries, including consumer electronics, automotive (particularly electric vehicles), healthcare, industrial automation, and aerospace, among others.
What are the advantages of using Wireless Power Transfer?
WPT improves convenience, safety, and mobility by eliminating the need for physical cables. It also reduces wear and tear on connectors, enhances user experience, and has the potential to power devices in areas where wiring is impractical or unsafe.
What are the types of Wireless Power Transfer technology?
There are several types, including inductive coupling, resonant inductive coupling, capacitive coupling, and microwave power transfer. Each type has its specific applications and efficiency levels.
What future developments can we expect in Wireless Power Transfer?
Future developments may include improved efficiency, longer range, integration into more consumer devices, and advancements in safety standards, making WPT more widely adopted across various industries